VIP Lighting: Nationwide retail and commercial lighting experts

A
AC (Alternating Current)
Current which flows in one direction and then the other, alternately.
Accent Lighting
Directional lighting to emphasize a particular object or draw attention to a display item.
Ambient Lighting
The general lighting present in an area – excluding task lighting and accent lighting
Amperes (AMPs)
A measure of electrical current. Watts divided by Volts.
B
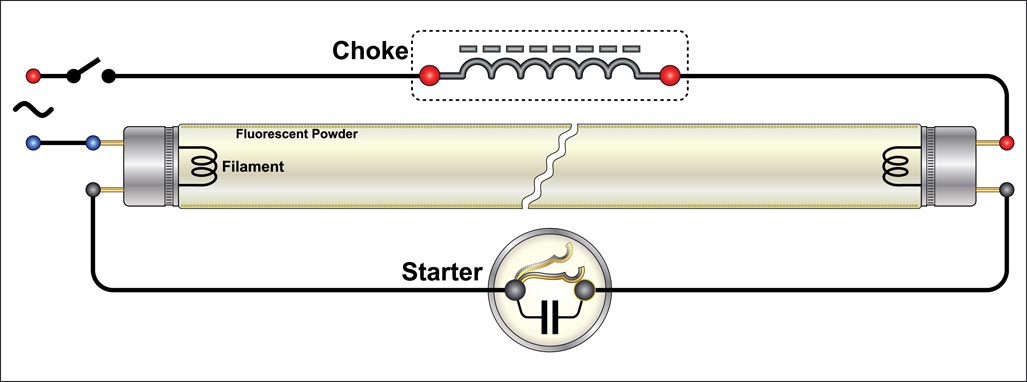
Ballast
A device which provides the necessary starting voltage and appropriate current to a fluorescent or high intensity discharge (HID) luminaire.
Ballast Factor (BF)
A ratio used to calculate the expected real-world performance of a lamp. Calculated as the difference between the expected performances of a lamp with a commercial ballast versus the measured performance of that lamp with a reference ballast. A ballast with a lower BF results in less light output and also generally consumes less power. Rated Lamp Lumens x Ballast Factor = Net Lumens.
Base or Socket
The socket is the receptacle connected to the electrical supply; the base is the end of the lamp that fits into the socket.
Bayonet
A style of bulb which uses keyways instead of threads to connect the bulb to the fixture base. The bulb is locked in place by pushing it down and turning it clockwise.
Bi-Pin
Any base with two metal pins for electrical contact. This is the typical base for a fluorescent tube of 1 to 4 feet in length. It consists of 2 prong contacts which connect into the fixture.

Bulb
A loose way of referring to a lamp. “Bulb” refers to the outer glass bulb containing the light source.
C
Ceramic Metal Halide (CMH)
A type of metal halide lamp that uses a ceramic material for the arc tube instead of glass quartz, resulting in better colour rendering and improve lumen maintenance.
Colour Rendering Index (CRI)
An international system used to rate a lamp’s ability to render object colours in comparison to a natural light source. The higher the CRI (based upon a 0 – 100 scale) the richer colours generally appear. CRI differences among lamps are not usually significant (visible to the eye) unless the difference is more than 3-5 points.

Compact Fluorescent lamp (CFL)
The general term applied to fluorescent lamps that are single-ended and that have smaller diameter tubes that are bent to form a compact shape. Some CFL’s have integral ballasts and medium or candelabra screw bases for easy replacement of incandescent lamps.
Cool White
A term loosely used to denote a colour temperature of around 4100K. The Cool White (CW) designation is used specifically for T12 and other fluorescent lamps using halo phosphors and having a CRI of 6.
D
Daylight Lamp
A lamp resembling the colour of daylight, typically with a colour temperature of 5500K – 6500K
Downlighting
Light which is cast downward from a fixture. The most common and direct form of lighting.
E

Efficiency
The efficiency of a light source is simply the fraction of electrical energy converted to light i.e. watts of visible light produced for each watt of electrical power with no concern about the wavelength where the energy is being radiated. For ex: a 100 watt incandescent lamp converts 7% of the electrical energy into light; discharge lamps convert 25% to 40% into light.
F
Flicker
The periodic variation in light level caused by AC operation that can lead to strobe effects.
Fluorescent Lamp
A high efficiency lamp utilising an electric discharge through inert gas and low pressure mercury vapour to produce ultraviolet (UV) energy. The UV excites phosphor materials applied as a thin layer on the inside of a glass tube which makes up the structure of the lamp. The phosphors transform the UV to visible light.
Four-Pin Compact Fluorescent Lamps (CFL)
A “plug-in” compact fluorescent lamp with 4 pins in the base to make electrical contact with the ballast.
H

Halogen Lamp
A halogen lamp is an incandescent lamp with a filament that is surrounded by halogen gases. The gases allow the filaments to be operated at higher temperatures and higher efficacies. The halogen participates in a tungsten transport cycle, returning tungsten to the filament and prolonging lamp life.
Heat Sink
A component or integral part of luminaire that conduct or diverts heat away from LED components.
High-Bay
Lighting used in industrial applications where the ceiling height is greater than 20 feet. Common in big box retail, industrial, warehouse and manufacturing spaces.
High Intensity Discharge (HID) Lamp
A general term for mercury, metal halide and high-pressure sodium lamps. HID lamps contain compact arc tubes which enclose mercury and various gases with other chemicals and operate at relatively high pressures and temperatures.
I
Illuminance
The “density” of light (lumens/area) incident on a surface. ie: the light level on a surface. Illuminance is measured in foot, candles or lux.
Instant Start or Rapid Start
Ballast starting type. Applies high voltage across the lamp with no preheating of the cathode.
K
Kelvin Temperature
A numerical scale used to describe the colour of light. Light with a lower Kelvin rating will have a more yellow tint, while light with a higher kelvin rating will have a bluer tint.

Kilowatt
1000 Watts.
Kilowatt Hour
1000 Watts used for one hour.
L
Lamp
The source of light in a fixture including the inner parts as well an outer bulb or tube…colloquially called a ‘light bulb’.

Lamp Disposal
Refers to the proper recycling of lamps containing mercury or other hazardous materials.
LED
Light Emitting Diode – commonly known as LED is a semiconductor device that emits visible light of a certain colour.
LED Driver
An electronic device which converts input power into a constant current source despite fluctuation in voltage. It protects LED from voltage fluctuations. In simple terms it is an electronic device which feeds input power to LED to produce light.
Light
Radiant energy that can be sensed or seen by the human eye. Visible light is measured in lumens.
Lumens
A unit of luminous flux; overall light output; quantity of light, expressed in lumens.
Luminaire
A complete lighting unit which contains a lamp, housing, ballast, sockets and any other necessary components. A luminaire is often referred to as a fixture.
Lux (lx)
A unit of illuminance equal to 1 lumen per square meter.
M
Mercury Lamp
A high-intensity discharge light source operating at a relatively high pressure (about 1 atmosphere) and temperature in which most of the light is produced by radiation from excited mercury vapour. Phosphor coatings on some lamp types add additional light and improve colour rendering.

Metal Halide Lamp
A high intensity discharge light source in which the light is produced by the radiation from mercury, plus halides of metals such as sodium, scandium, indium and dysprosium. Some lamp types may also utilise phosphor coatings.
MR-16 and MR-11
A line of low voltage compact reflector lamps used for accent and spot lighting. The 16 and 11 refer to 16 eights of an inch diameter and 11 eighths.
P
Phosphor
An inorganic chemical compound processed into a powder and deposited on the inner glass surface of fluorescent tubes and some mercury and metal halide lamp bulbs. Phosphors are designed to absorb short wavelength ultraviolet radiation and to transform and emit it as visible light.
Pulse Start
An HID ballast with a high voltage ignitor to start the lamp.
Q
Quad
Generally refers to a compact fluorescent lamp (CFL) containing 4 U-shaped tubes
Quartz
A name for fused silica or melted sand from which many high-temperature containers are fashioned in the lighting industry. Quartz looks like glass but can withstand the high temperatures needed to contain high intensity arc discharges.
R
Rapid Start
A method of starting typically associated with magnetic ballasts; where a low filament voltage is applied to preheat the cathodes.
Rapid Start Lamp
A fluorescent lamp with two pins at each end connected to the filament. The filaments are heated by the ballast to aid in starting. Some rapid start lamps may be instant started without filament heat.

Rated Lamp Life
For most lamp types, rated lamp life is the length of time of a statistically large sample between first use and the point when 50% of the lamps have died. It is possible to define “useful life” of a lamp based on practical considerations involving lumen depreciation and colour shift.
Re-Strike
Refers to the restarting of a previously operating lamp shortly after turnoff. Metal halide lamps typically require a minimum of 4 – 15 minutes to restart after turn-off.
S
Self-Ballasted Lamps
A discharge lamp with an integral ballasting device allowing the lamp to be directly connected to a socket providing line voltage. (See CFL)
Starter
An electronic module or device used to assist in starting a discharge lamp, typically by providing a high-voltage surge.
T

T5
5/8”diameter fluorescent lamps. “T” stands tubular, while the number “5”stands for the 5 in 5/8”. Therefore a T8 lamp would be a Tubular 8/8”, or 1”diameter lamp. 280014479
T8
1”dimeter fluorescent lamps.
T12
12 eighths of an inch, or 11/2 inches
Task Lighting
Supplemental lighting provided to assist in performing a localised task Ex: a table lamp for reading or an inspection lamp for fabric inspection
Two-Pin Compact Fluorescent Lamps
Type of lamps that have the glow bottle starter built into the base of the lamp. Traditionally 2-pin lamps are designed to work with electromagnetic ballasts.
V
Valance Lighting
Lighting from a light source on a wall typically above eye level, shielded by horizontal panels. The light may be upward or downward directed.

Volt
A measure of electrical pressure” between two points. The higher the voltage, the more current will be pushed through a resistor connected across the points. The volt specification of an incandescent lamp is the electrical “pressure” required to drive it at its designed point. The “voltage” of a ballast refers to the line voltage it must be connected to. 204540481
Voltage
A measurement of the electromotive force in an electrical circuit or device expressed in volts.
W
Warm White
Refers to a colour temperature around 3000K, providing a yellowish-white light.
Watts
A unit of electrical power. Lamps are rated in watts to indicate the rate at which they consume energy.




















